Middle East Opportunities: Qatar's Economic Growth Strategy(Part 2)
Diversification Clusters
In order to achieve sustainable economic growth, the NDS3 identified a set of diversification clusters to be developed. Again, these industries mostly cover digitalisation, technology and sectors that improve the country’s overall attractiveness to talent, including tourism, education, health and the creative industries. Concurrently, exports form the core of these growth clusters, supported by the development of manufacturing and logistics.
Located in the centre of the Persian Gulf, Qatar has the ideal geographical location to be a regional logistics hub. Notably, its logistics sector is one of the country’s fastest‑growing industries, achieving 26% growth in 2022 and reaching US$10 billion in market size.Airport Council International’sstatistics show that theHamad International Airportin Doha was the world’s 8th busiest airport by air cargo throughput globally and the 4th busiest in Asia in 2023. The Hamad Port is the world’s 8th largest port in terms of capacity, which bodes well for the country’s ambitions to further develop its logistics sector and for global logistics companies to leverage Qatar as a regional hub for logistics and warehousing. Hong Kong businesses can look to leverage Qatar’s advantageous position as a regional distribution centre to expand their overseas operations, capture a share of the rapidly growing consumer market in the MENA (Middle East and North Africa) region, and facilitate trade activities along the China‑Middle East corridor.
Underscoring the potential of Qatar’s logistics industry, numerous companies have already invested inRas Bufontas, an airport free zone, andUmm Al Houl, a seaport free zone, both of which are regulated by theQatar Free Zone Authority. Prominent examples includeUPS,VolkswagenandDHL.6
On the industrial and manufacturing front, Qatar aims to boost its non‑hydrocarbon exports to QAR 49 billion (US$13 billion) and attract annual industrial investment of QAR2.75 billion (US$740 million) by 2030. While the hydrocarbon sector is expected to remain dominant in the short to medium term, Qatar envisions developing smart and advanced manufacturing to achieve its diversification goals. With its small but well‑educated population, developed infrastructure and cheap energy, the country has identified growth opportunities in manufacturing through embracing IoT solutions, 3D printing, AI and industrial robots.
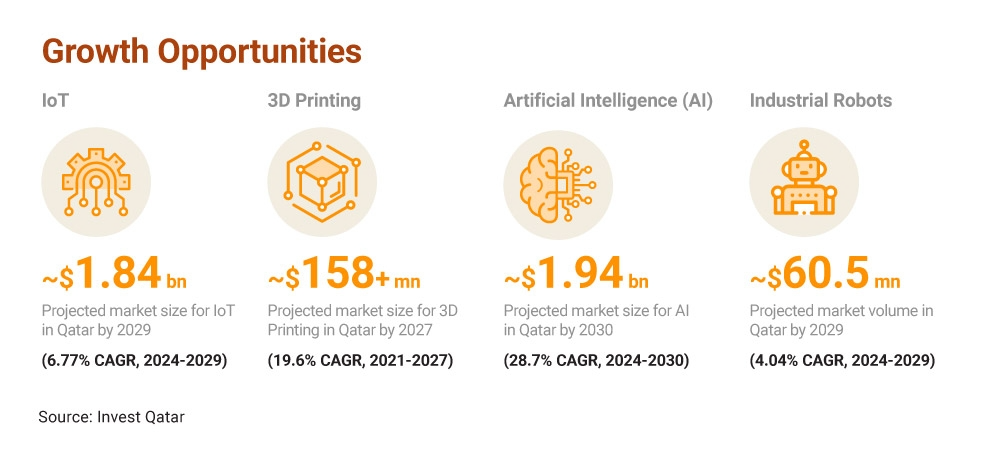
IoT, 3D printing, AI and industrial robots represent growth opportunities for Qatar’s manufacturing sector. (Source: Invest Qatar)
NDS3 Diversification Clusters | |
Growth Clusters | Manufacturing: Expand manufacturing in chemicals and low-carbon metal sectors Logistics: Establish country as re-export hub for select high-value products and strengthen air transport position globally Tourism: Re-position as tourism destination of choice for families and develop business and event tourism |
Enabling Clusters | IT & Digital: Develop digital economy and long-term strategic capabilities in AI as well as expertise in other emerging technologies Financial Services: Develop niche specialisations (including “insurtech”), strengthen asset management capabilities, deepen capital market resources Education: Promote country as a higher education hub, develop specialisations and increase private sector participation |
Resilience Clusters | Food & Agriculture: Boost food security and develop long-term specialisation (such as agritech) Health services: Increase private sector participation, develop medical tourism and build capability in specialist areas (such as precision medicine) |
Future Clusters | Explore development over time of additional clusters, centred on areas such asgreen techand national assets, including those in themedia and creative industries |
Open for Investment
In common with its neighbours, Qatar is keen to attract more FDI. In 2019, it enabled full business ownership of non‑Qatari capital investment, and it is expected that country will enact further regulatory reforms and formulate business friendly laws in view of the region’s fierce competition for FDI and pursuit of economic diversification.
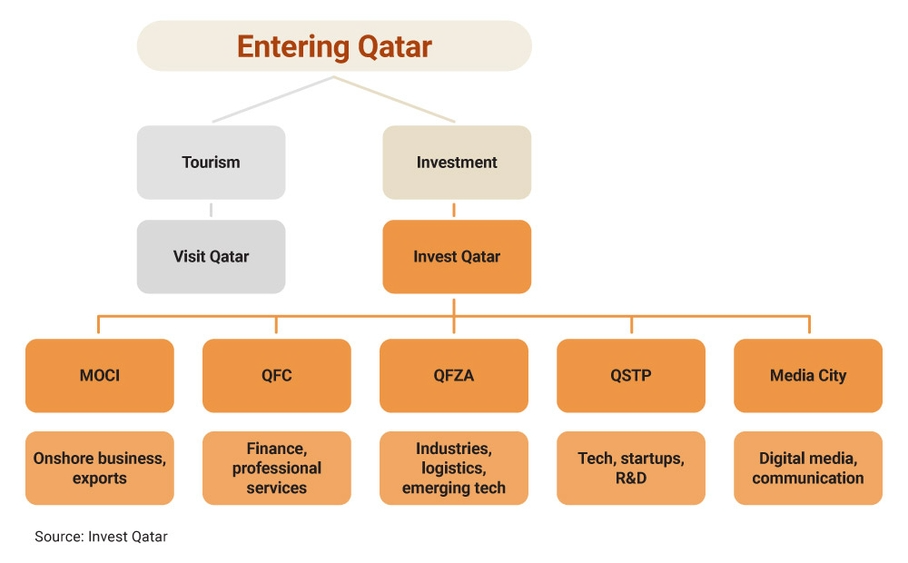
Qatar offers five different licensing platforms where businesses can register depending on their business nature and purpose:
I. Ministry of Commerce and Industry (MOCI)
a. Exemption of customs fees on imports of necessary machinery, equipment and raw materials, or of part‑manufactured goods necessary for production
b. Foreign investors can transfer any amount related to their investment to and from any external destination without delay
II. The Qatar Financial Centre (QFC)
a. Up to 100% foreign ownership
b. 100% repatriation of profits
c. English common law, independent court and dispute resolution centre
III. The Qatar Free Zones Authority (QFZ)
a. 100% foreign ownership
b. 20‑year corporate tax exemptions
c. Zero income tax and customs duties on imports
IV. The Qatar Science and Technology Park (QSTP)
a. Up to 100% foreign ownership
b. Exemption on corporate tax, personal income tax and customs duties
c. No restrictions on repatriation of capital, profit and salaries
d. Supporting infrastructure
V. Media City Qatar
a. 100% foreign ownership
b. Flexible employment and immigration regulations
c. 20‑year corporate tax holiday
d. 100% repatriation of capital and profits
e. Exemptions from import and export tariffs
Instead of directly approaching the respective licensing platforms, Hong Kong businesses interested in investing in Qatar can approachInvest Qatarfor more information and advice before deciding on the best way to tap into the Qatari market.7 Businesses interested in bidding for Qatari projects should acquaint themselves with relevant regulations and requirements. For instance, local laws might be applied for dispute resolution unless specified. Additionally, while foreign firms are not required to have a local presence, firms that do, or which source or hire locally, may enjoy advantages.




















































First, please LoginComment After ~