Middle East Opportunities: Qatar's Economic Growth Strategy(Part 1)
Middle East Opportunities: Qatar’s Economic Growth Strategy
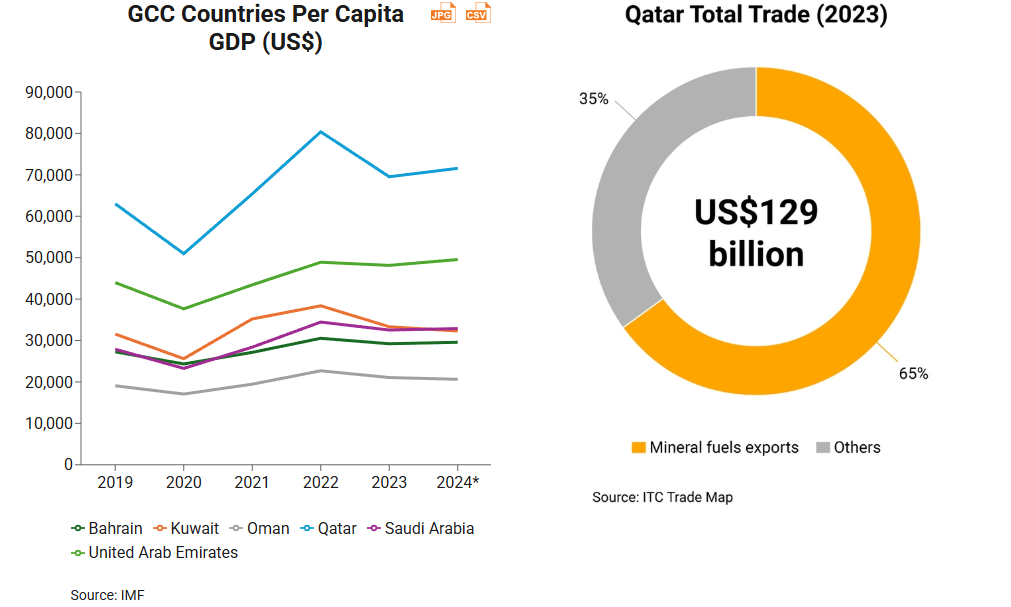
Qatar’s per capita GDP of about US$70,000 is not only the highest in the region, but also one of the highest in the world. However, the greater part of that is contributed by the country’s rich natural gas reserves. Qatar’s hydrocarbon revenues accounted for 87% of Qatari government revenue between 2017 to 2021, underscoring the country’s high dependency on the energy sector. This is also illustrated by Qatar’s merchandise trade: currently almost two‑thirds of that trade is comprised of mineral fuel exports.
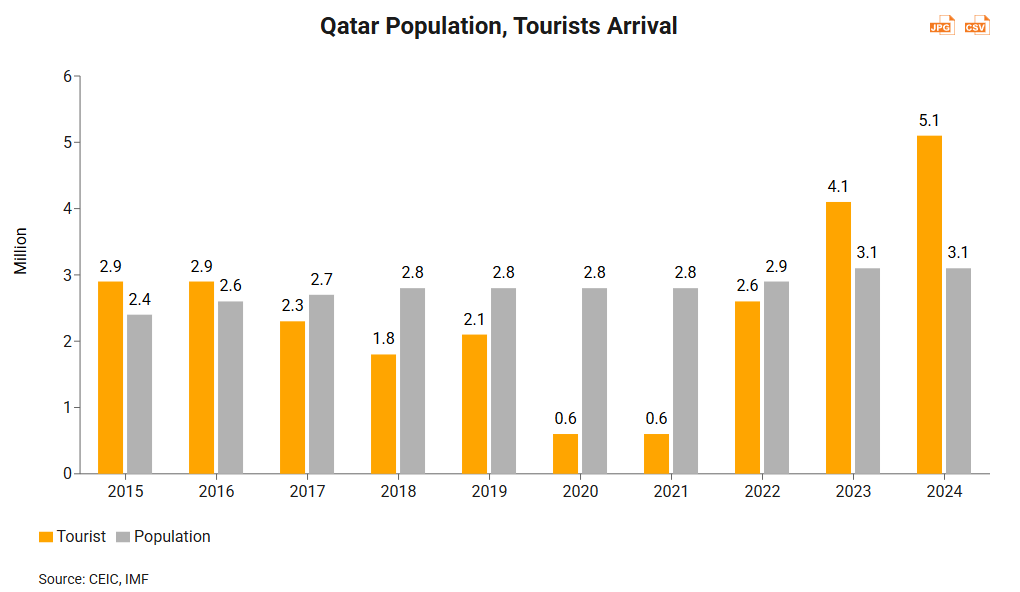
Having a land mass about 10 times that of Hong Kong, Qatar’s population is less than half of Hong Kong’s, standing at about 3 million. However, Qatar has experienced significant population growth over the past few years, rising from just 2.75 million people in 2021. Similar to its neighbour, the UAE, Qatar has a diverse population mix. Roughly 88% of the Qatari population are expats and native Qataris only number about 360,000. It is therefore safe to conclude that Qatar’s population has grown as a result of massive inflow of expats, highlighting the country as an attractive place to live and work. While the Qatar FIFA World Cup 2022 could be considered a major driver of this due to huge demand for labour in preparation for world football’s flagship event, the population has continued to increase in subsequent years. According to surveys, Qatar is one of the top 10 countries in which to live and work globally for expatriates, the safest country in the world, and the country with best healthcare system in the Arab world.
Following the Covid‑19 pandemic and a crisis in Gulf Cooperation Council relations, which ended in 2021, Qatar has flourished as an open and vibrant economy, as exemplified by its large number of tourist visitors. Since the World Cup in 2022, the number of tourists visiting Qatar increased by 58% in 2023 and 25% in 2024, reaching over 5 million. Qatar aims to attract 6 million visitors and generate QAR 34 billion (US$9 billion) in destination spending by 2030.
National Development Strategy (2024-2030)
With the aim of developing a sustainable, diversified and knowledge‑based economy, Qatar last year unveiled a national development blueprint – Nation Development Strategy (2024‑2030) (NDS3) – in which it listed out a wide array of targets to be achieved by 2030.
These targets can be divided into seven pillars: (1) Sustainable Economic Growth; (2) Fiscal Sustainability; (3) Future‑Ready Workforce;
(4) Social Cohesion; (5) Quality of Life; (6) Environmental Sustainability; and (7) Government Excellence. Broadly, these target two core approaches to creating sustainable economic growth and creating an attractive place to live and work for global talent.
Selected 2030 targets and actions outlined in NDS3 | |
2030 Targets | Implementation |
(1) Sustainable Economic Growth | |
|
|
(2) Fiscal Sustainability | |
|
|
(3) Future-Ready Workforce | |
|
|
(4) Social Cohesion | |
|
|
(5) Quality of Life | |
|
|
(6) Environmental Sustainability | |
|
|
(7) Government Excellence | |
|
|
* Achieving 4-Gigawatt renewable energy capacity is equivalent to increasing renewable energy mix from 5% to 18% | |
It is worth noting that digitalisation is one of key actions that Qatar will adopt in order to achieve its 2030 targets. This means that digital solution service providers and innovation and technology companies should pay close attention to opportunities in Qatar.
Businesses can target specific digitalisation projects in the private sector, especially in the banking and financial sectors. With the ambition of enhancing efficiency and expanding their operations globally, Qatar’s financial institutions are keen on adopting fintech solutions such as insurance technology (Insurtech), digital payments, innovative financial products and robotic process automation. According to HKTDC interviews with local industry experts, fintech adoption and digitalisation are a key focus and Qatari businesses are open to foreign solutions, thereby providing ample room for collaboration with foreign tech companies.
Green building solutions and agritech, two other areas of focus in the NDS3, also present opportunities. Notably, the country envisions achieving 100% self sufficiency in fresh poultry and dairy produce, according to Invest Qatar.1 In addition, Qatar has been rapidly expanding its infrastructure, in addition to developing hotels and expanding residential and commercial real estate, thereby driving significant demand for green building solutions. The Hong Kong Startup Survey2 and HKTDC Research’s reports show that green building3, sustainable tech and food tech4 are among Hong Kong’s strongest areas of expertise, underscoring the potential for collaboration between Hong Kong and Qatar.
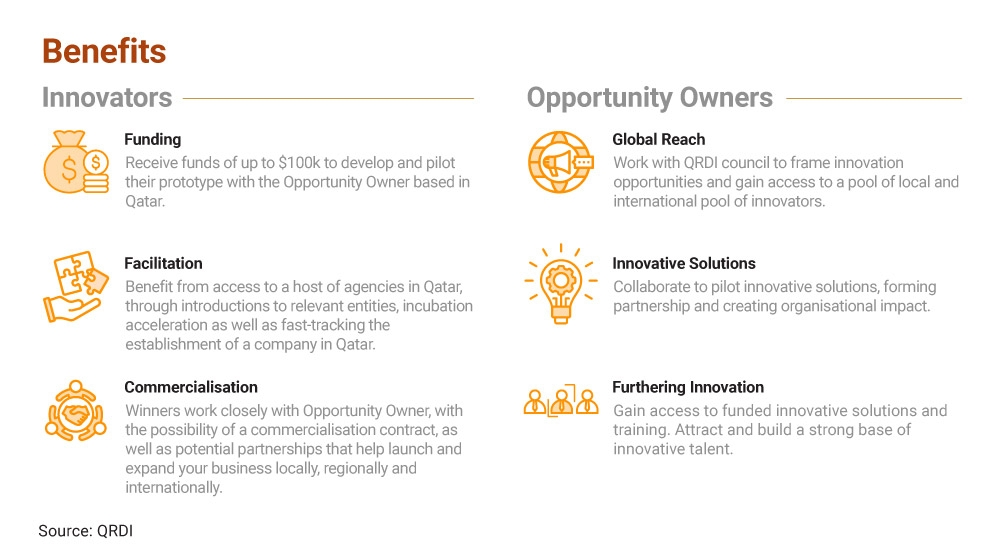
In fact, Qatar has been actively welcoming foreign innovation and technology companies and solutions into the country. For example, there are various competitions funded by Qatari public entities for global startups to join. The Qatar Open Innovation programme, launched by the Qatar Research Development and Innovation Council (QRDI), offers opportunities for global innovators to explore the Qatari market. Under the programme, large Qatari enterprises and government agencies (called “opportunity owners”) list out challenges that they are facing, and global innovators are invited to propose their solutions to solve these challenges. Selected candidates receive funding of up to US$100,000 and the opportunity to pilot their solution or prototype with the opportunity owners in Qatar, enabling them to leverage Qatar as a testbed and hone their solutions.5 The competition winners can also work closely with opportunity owners to commercialise their solutions. In addition to holding competitions, Qatar also collaborates with global researchers in priority areas. According to Qatari sources, the country currently has more than 10 collaborative research projects in progress with Hong Kong universities, spanning pillars such as medical and health sciences, agriculture, and engineering and technology.





















































First, please LoginComment After ~